-
Learning test
-
Depth estimation test
-
Sensory skills test
-
Hand coordination test
-
Testing the ability to recognize signs with feet
-
Aerobic power test
-
Entropy test
-
Testing reactions to different signals
-
Visual error test, measurement of eye fatigue
-
Optometry test
-
Testing visual stimuli
-
Testing people's mobility



-
General MachinesThis laboratory works with general machines, which include lathes, milling machines, drills, grinding machines, and crank saws. These devices are controlled manually and cannot connect to a computer, but they can be controlled by advanced computer software. Working with these production machines helps students learn how they work, understand their advantages and disadvantages while making different parts, and eventually use these devices to optimize parts production lines.

-
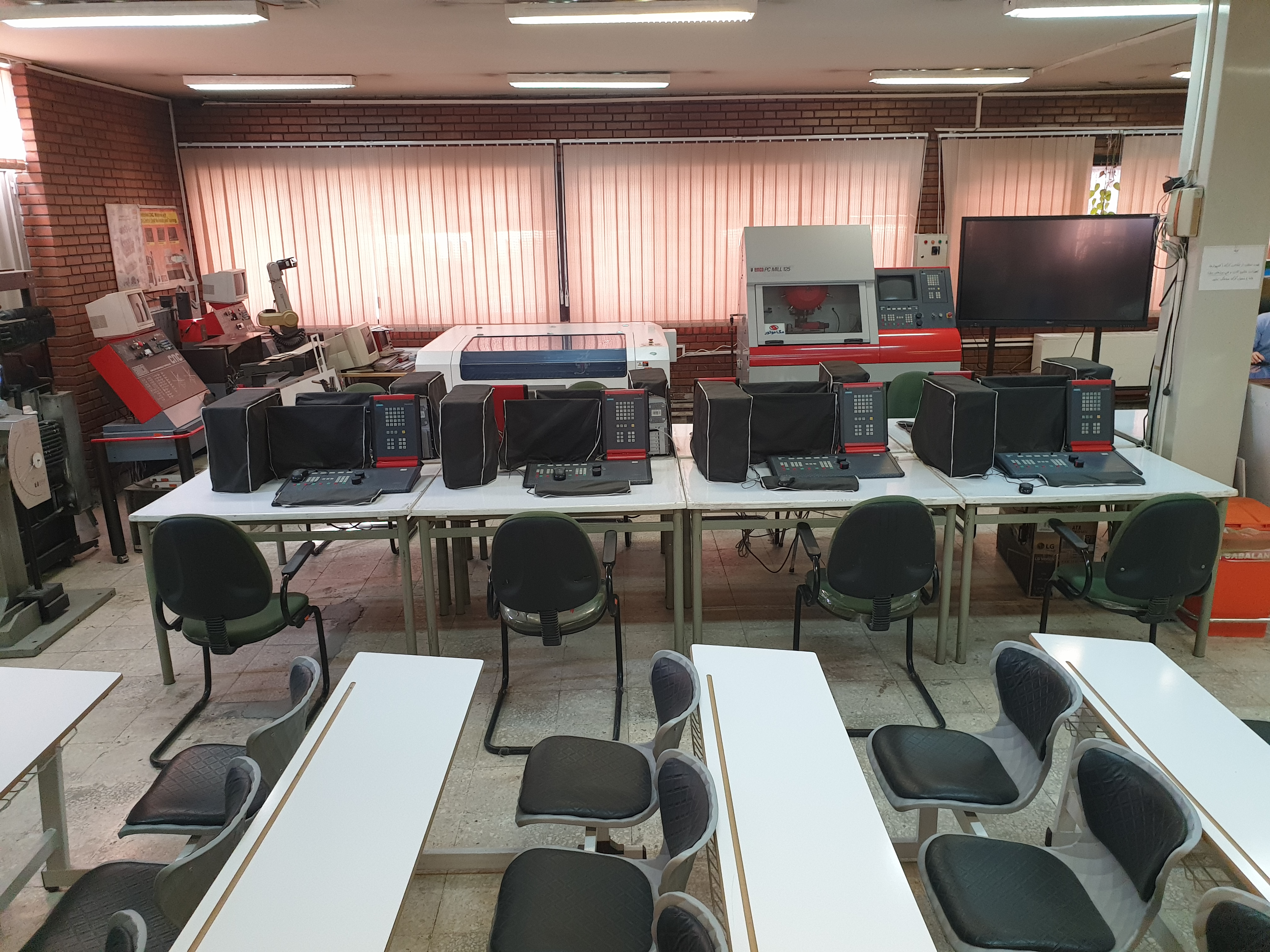
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines and their softwareUnlike the machines described in the previous section, CNC machines work automatically and are computerized. Students learn to work with these machines and computer software related to them, i.g. g-code machine language, CAD, CAM, and WIN NC software, to design parts and make them using CNC machines. Finally, students compare CNC machinery with general machines.

-
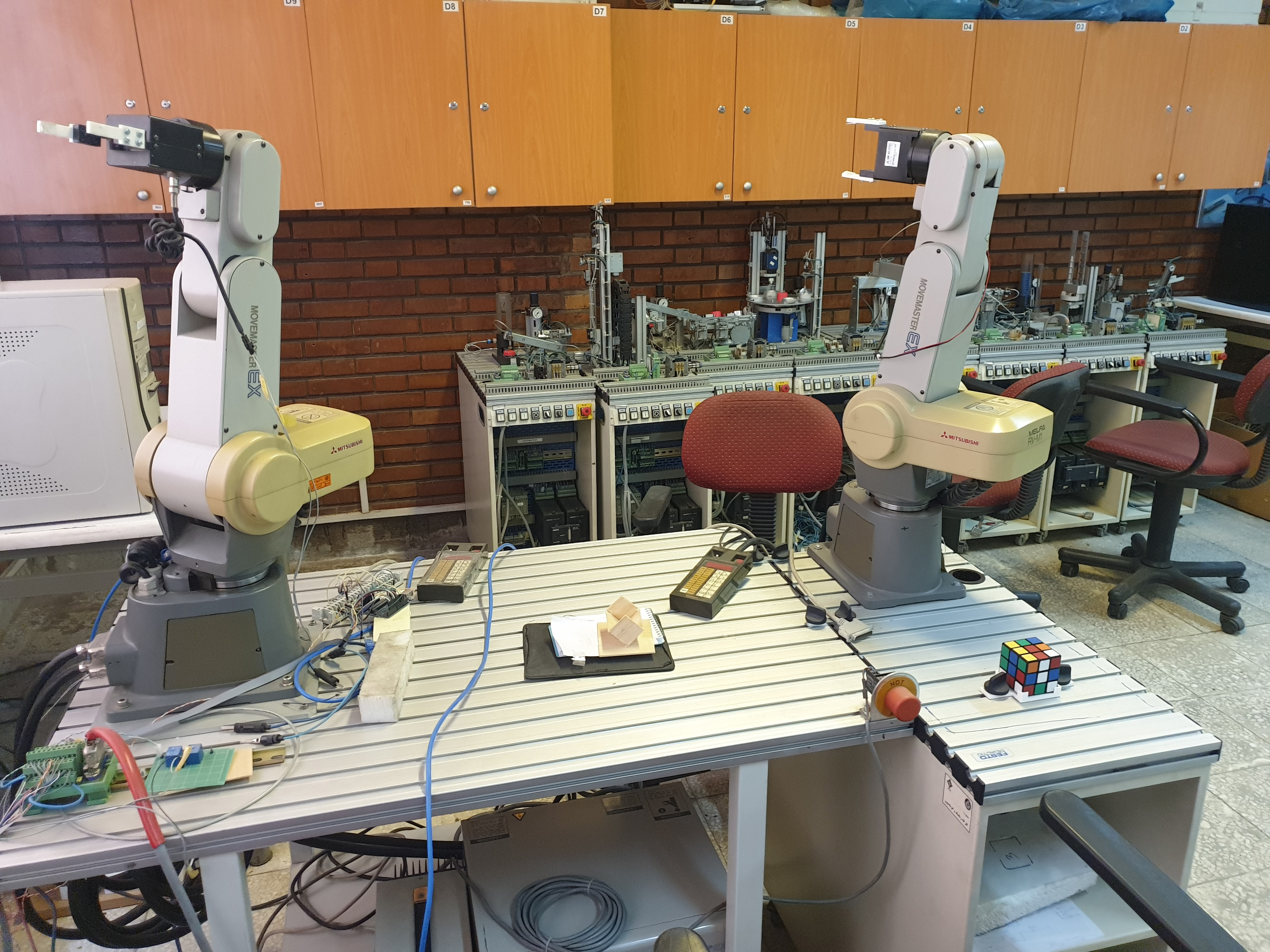
Industrial RobotsStudents learn how robots work, observe their role in industrial automation, and generally learn about the features, advantages, and disadvantages of using them in parts production lines. Students are first introduced to programming and working with robots; then, they learn to work with robots to communicate with each other in the form of laboratory production systems. All the robots in the lab are Movemaster EX 5 degrees of freedom robots, all of whose joints are Revolute type.

-
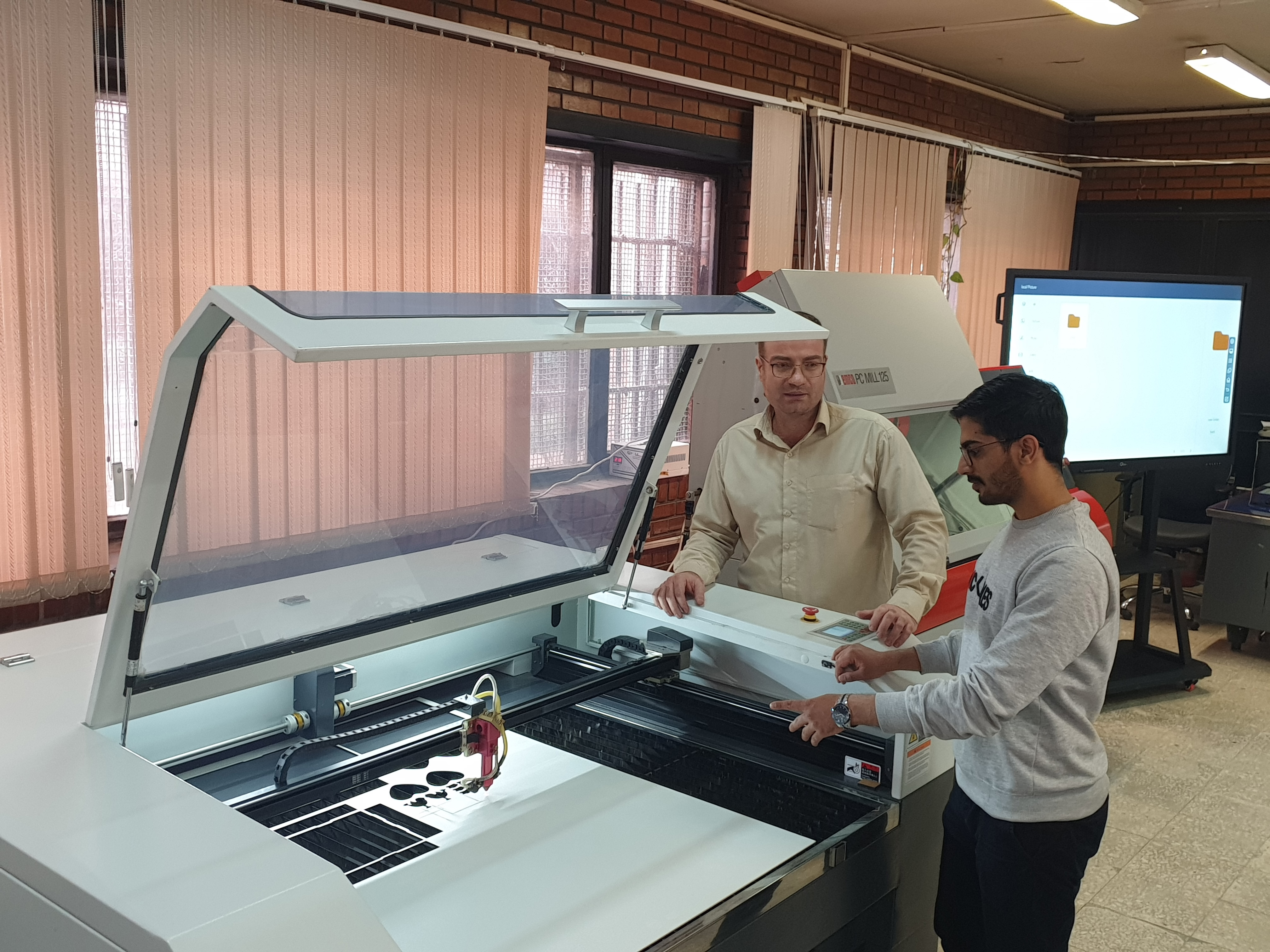
laser CutThe laser device uses laser rays to cut or create different designs and patterns on objects. Accuracy and high speed of cutting are among the benefits of these devices.

-
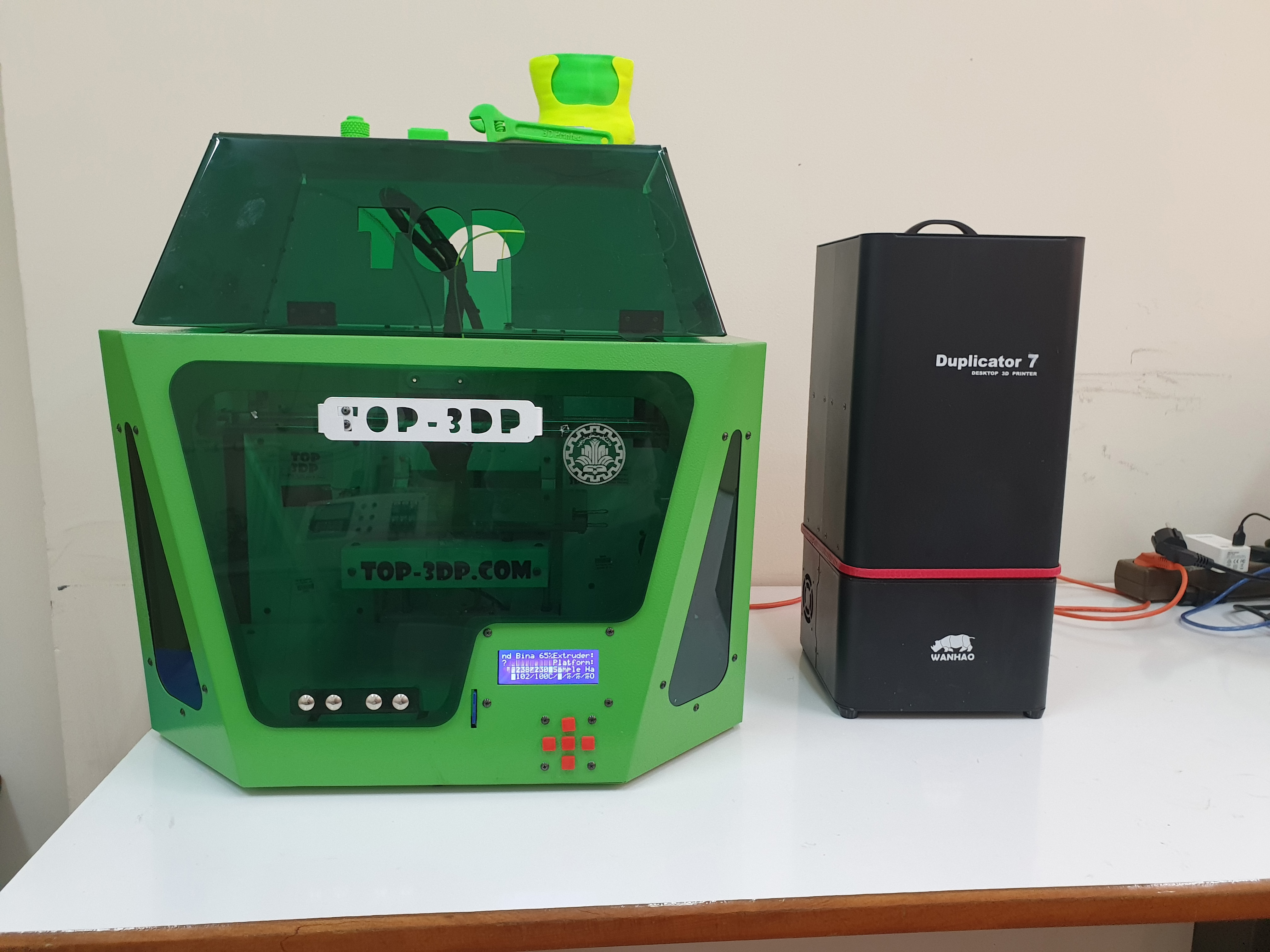
Layered construction and productionLayered construction is a fast prototyping method. A 3D scanner or computer software (CAD) prepares the desired sample design and the path codes for adding materials to produce the sample. This lab aims to provide research services in making samples with 3D printers.

-
Hydraulic and pneumatic control systemsThe hydraulic-pneumatic laboratory help students understand the principles of using fluids in power transmission and forming various hydraulic-pneumatic circuits. It is also possible to close pneumatic circuits in connection with PLC controllers to better understand their application in industrial automation.
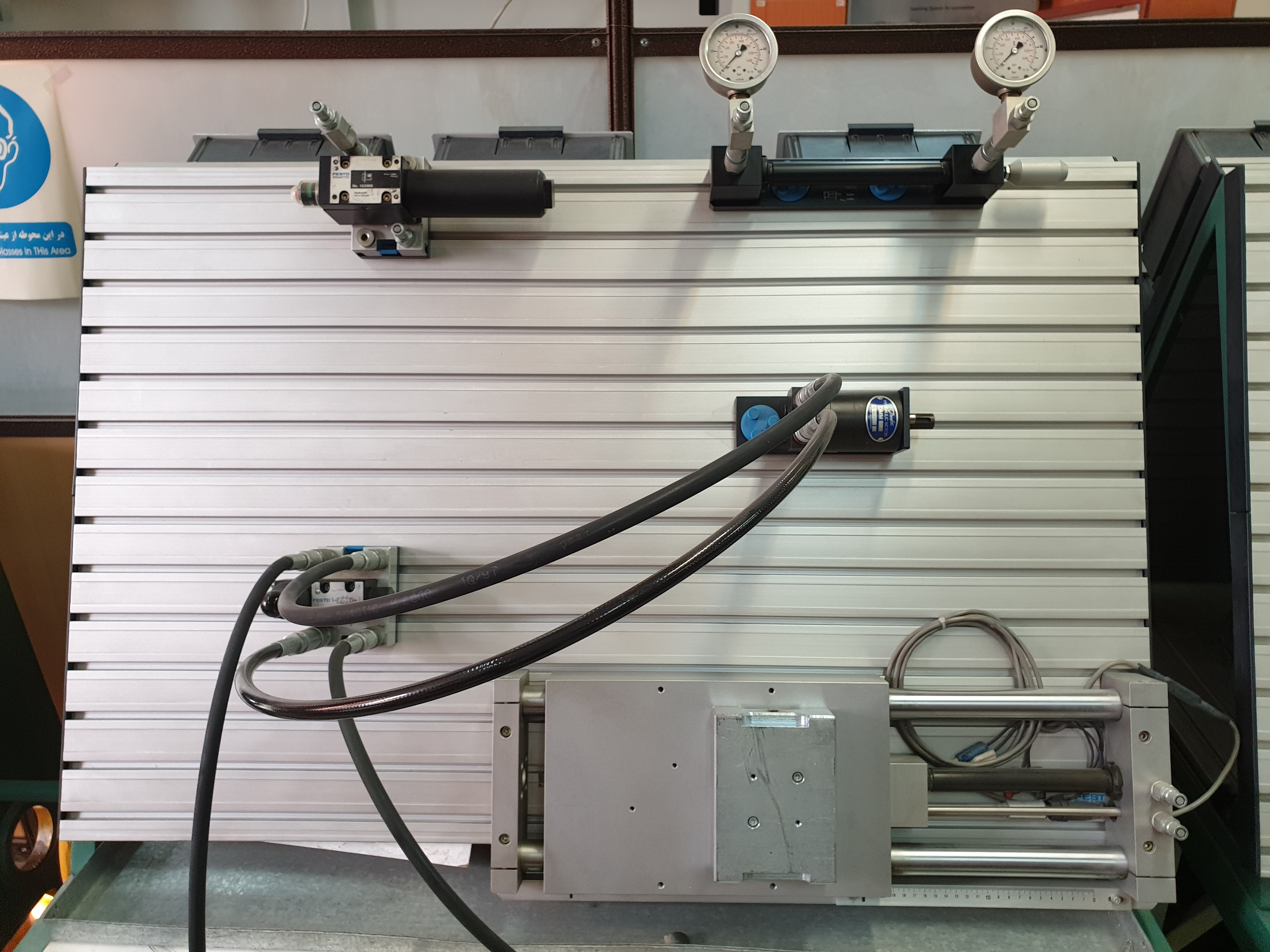

-
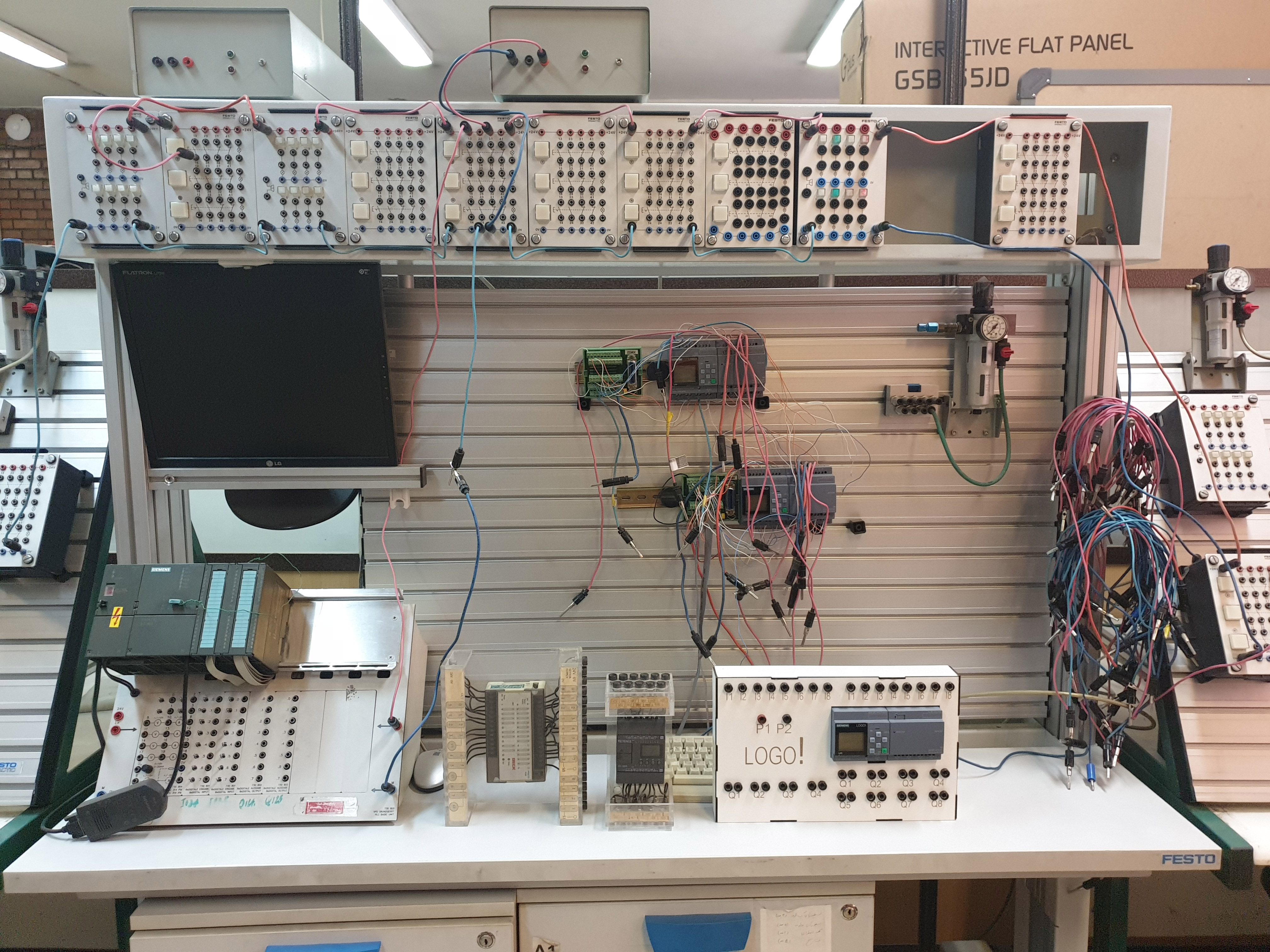
PLC logical control systemsProgrammable logic controllers, or PLCs, play a fundamental role in industrial automation systems. After learning the principles of programming and setting up these controllers, students in the logical control systems laboratory use them in laboratory production lines and systems and close different pneumatic circuits. This experiment helps industrial engineering students to learn about the benefits of using controllers and use them in the design of various production lines.
-
Mechanical TestsIt is essential to know the mechanical properties of materials in different stages of manufacturing and production of parts, such as design, production, and quality control stages. In this regard, the production method laboratory has the equipment to perform three mechanical tests: impact, hardness, and torsion. Students can compare the quality of the product in different production methods while learning how to perform these tests.
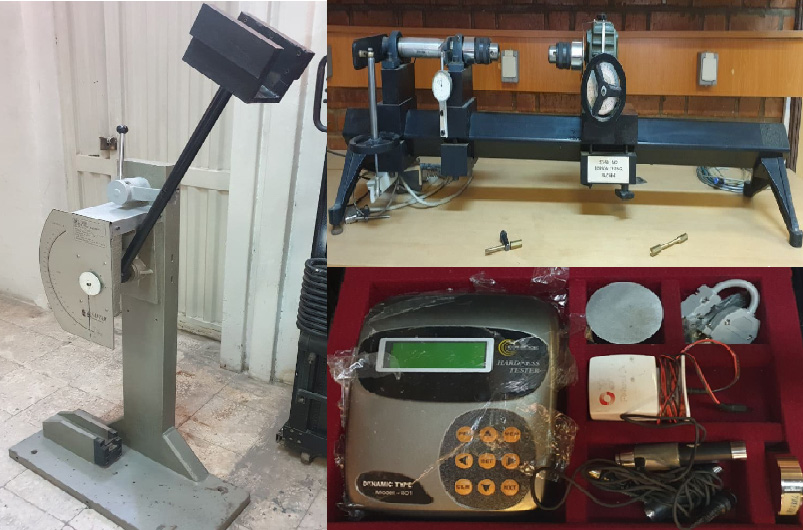

-
Heat Treatment FurnaceMaking some parts and samples requires heat treatment. For example, making metal parts by casting requires melting the metal in a heat treatment furnace. This equipment familiarizes students with different manufacturing methods, and students can use it in line with their research activities.

-
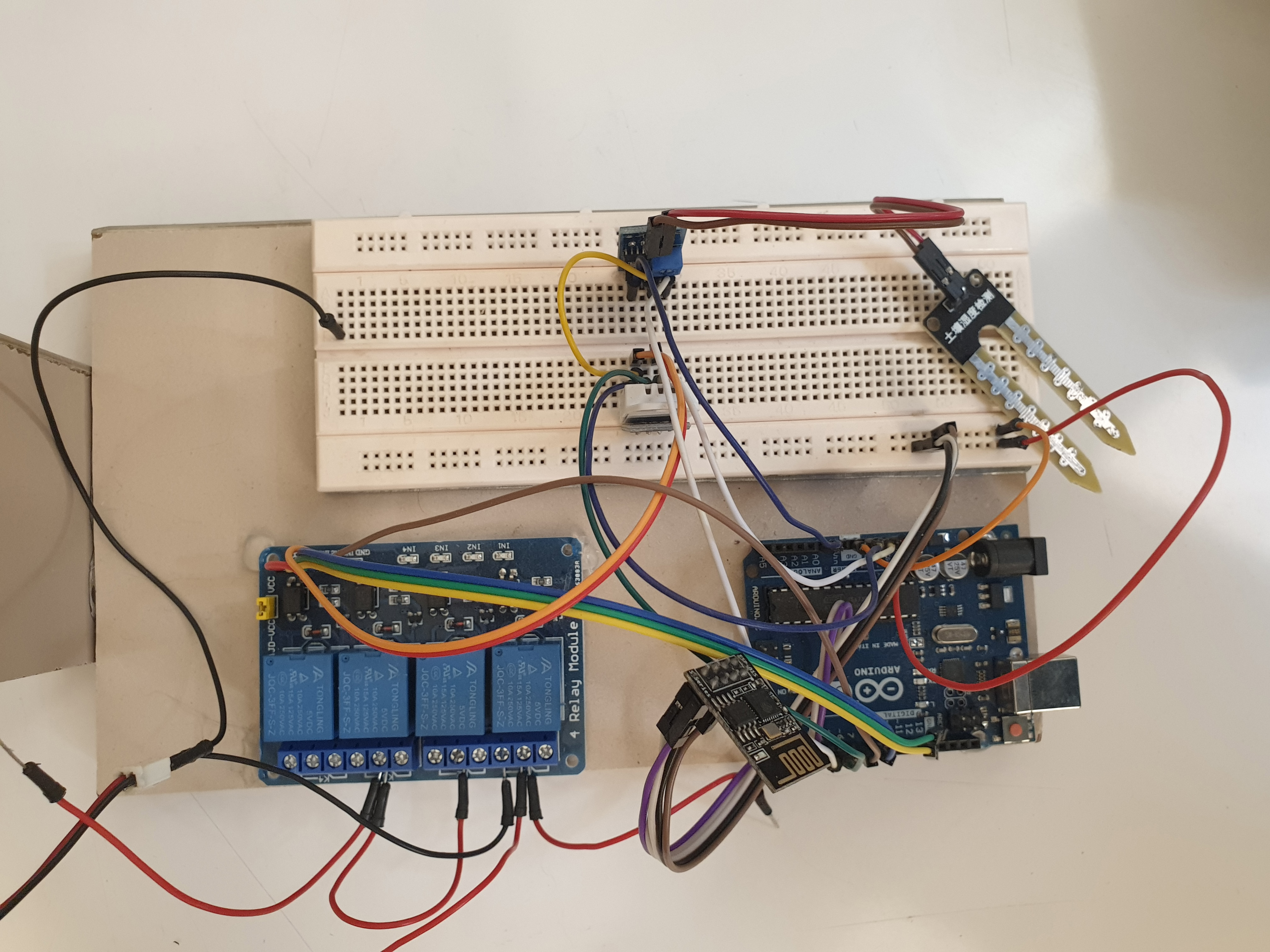
Internet of Things (IOT) Lab
The activities of this laboratory include:
-
Providing an experimental platform for collecting information from the physical world.
-
Transferring them to the control center.
-
Processing data
This lab is equipped with devices to monitor energy consumption, sensors of environmental parameters such as humidity, temperature, etc., and the necessary communication infrastructure. While conducting experimental and research activities in the Internet of Things, students in this laboratory simulate smart factories, cities, agriculture, etc., on a smaller scale and gain experience in this field.
-
-
FMS and Modular Production Systems
The main feature of flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) is their diversity and flexibility in production and automation. These systems usually use four types of equipment:
-
Numerical control (NC) machines and CNC computer numerical control
-
Automatic parts transportation systems
-
Coordination of computer control systems
-
Components such as measuring apparatus, washing, etc.
In modular production systems, the production process happens in multiple cells, where each cell performs a specific activity in testing, processing, control, assembling, etc. In the laboratory of production methods, with the provision of equipment for these two types of production systems, it has become possible to carry out research activities in this field.
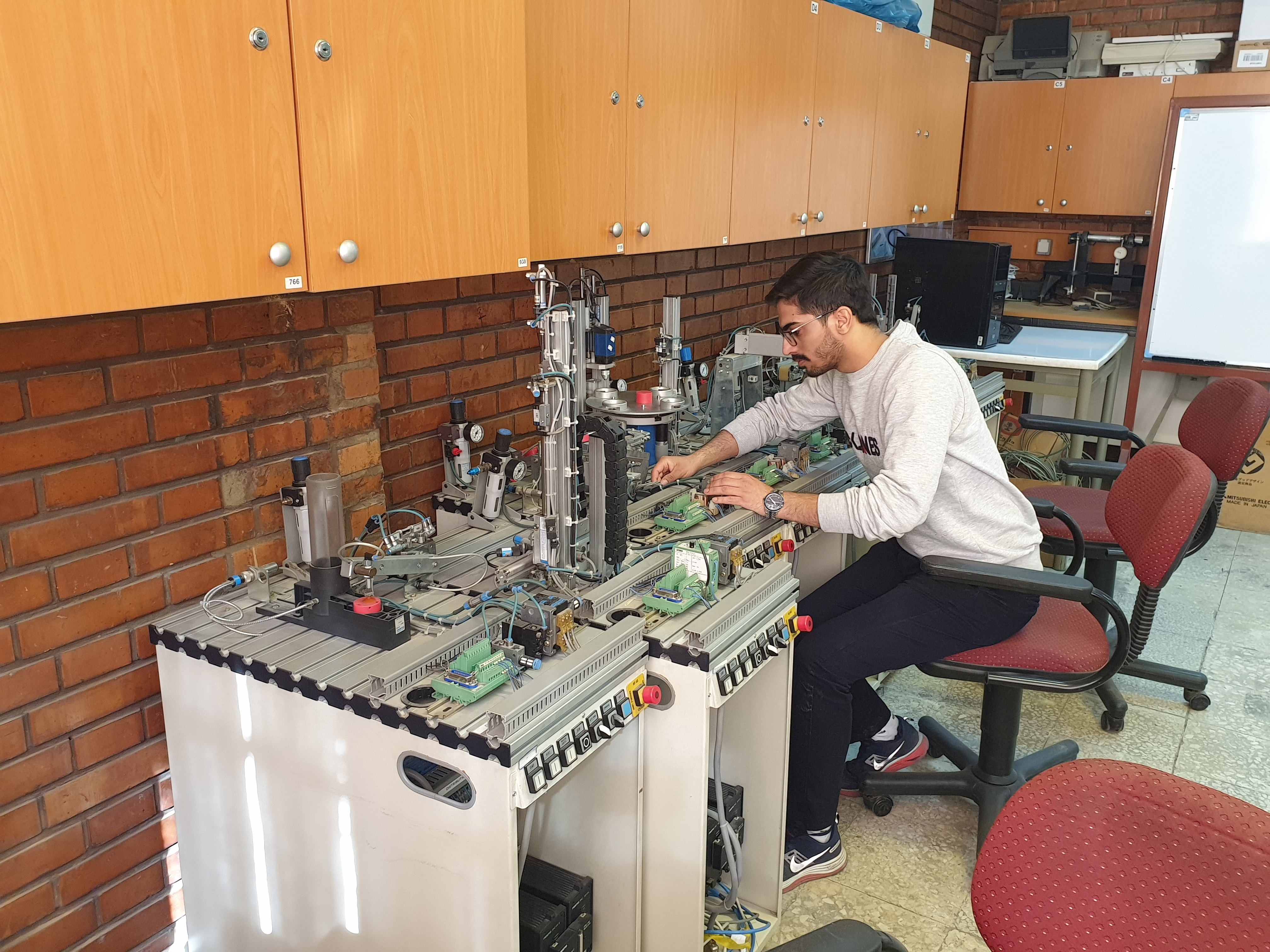

-
-
Virtual reality lab (VR)
This laboratory was established in 1400 to introduce students to virtual reality. Virtual reality is a new field that can be used in all areas, including education. Virtually visiting production lines is one of the activities done in the production method laboratory by virtual reality cameras.

This laboratory is designed to familiarize with the fields of study of work measurement method and learning curve. The designed tests include familiarization with common tools in industrial works and how they work, work table design, assembly line balance, study of movement in work, the role of using restraints in industrial works, selection of optimal equipment in parts inspection, pin timing and Lattice board through chronometer, tests to determine performance coefficient in time measurement, time measurement of power distribution box through MTM and MOST methods, time measurement by work sampling method and learning curve test. The purpose of conducting the above experiments is to acquaint the students with the real cases of work and to present the idea of improvement in performing various tasks and to familiarize them with the practical way of measuring time at work.

